
Table of Content
- An Overview of Zero Trust Architecture for Security Management
- Real-World Impacts of Cloud Security Incidents on Businesses
- Cloud Security Best Practices to Prevent Data Breaches
- Zero Trust Architecture: Foundational Principles
- The Value of Adopting a Zero Trust Approach
- Why Korcomptenz?
- Embracing Managed Cloud Security Services
In 2024, cybersecurity faces complex, multi-layered threats, requiring advanced cloud security due to increased digital technologies and attack vectors. The cloud, including IaaS platforms, is not naturally secure and has its own vulnerabilities.
- Data shows that 45 percent of breaches are cloud-related.
- 80 percent of companies faced cloud security incidents over the past year.
- Over 8 million records were exposed globally due to data breaches in Q4 2023.
This change necessitates a detailed understanding of threat trends and the use of more advanced defense strategies like the use of zero trust cloud security solutions. Last year, the global Zero Trust security market was valued at over $31.6 billion and is projected to grow to $133 billion by 2032. The focus is on both preventing known threats and foreseeing and reducing new vulnerabilities with managed cloud security services
Security leaders are adopting zero trust with cloud security solutions, and many enterprises are following suit. A survey reveals that 89 percent consider security vital for successful cloud deployment.
Zero Trust architecture is key in fighting rising cyber threats, shifting from “trust but verify” to “never trust, always verify,” addressing the weaknesses of traditional perimeter-based security models.
An Overview of Zero Trust Architecture for Security Management
Zero trust in cloud security requires constant verification of all devices and users, regardless of their location. It emphasizes strict authentication, minimal access, and micro-segmentation to minimize the attack surface and enhance security.
Compared to conventional security practices, zero trust delivers a more nuanced and flexible approach to network protection, ensuring cloud security best practices.
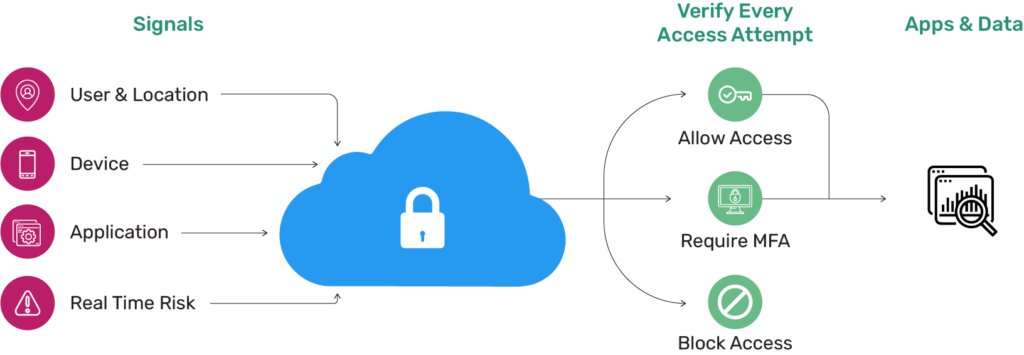
Traditional models focused on perimeter defenses, often allowing attackers easy access if breached. Zero trust cloud security also enforces strict access controls and continuous monitoring, containing damage from breaches. However, implementing zero trust can be complex and resource-intensive.
Real-World Impacts of Cloud Security Incidents on Businesses
- A major social media platform suffered a massive breach, revealing 530 million personal records.
- In 2021, LinkedIn faced a data scraping breach impacting 700 million profiles, mostly public.
- In August 2021, a multinational major was breached by LockBit ransomware, which stole and leaked proprietary data and compromised customer systems.
Cloud Security Best Practices to Prevent Data Breaches
Here are some of the top practices associated with cloud security services to avoid risks:
- Define clear business objectives
- Identify and understand the protection surface
- Map out network assets
- Establish strong device identities
- Implement centralized monitoring
- Avoid trusting your local network by default
- Segment your network
- Use multiple verification methods
- Enforce zero-trust policies
Zero Trust Architecture: Foundational Principles
Identity Verification: Zero Trust architecture requires continuous identity verification for both users and devices, scrutinizing every access request. This ongoing validation ensures access rights match current roles but can complicate user management and impact experience if not managed well.
Least Privilege Access: It’s a core element of zero trust, ensuring users receive only the essential permissions for their roles. This minimizes internal data breach risks and limits the impact of compromised credentials.
Micro-segmentation: This means breaking the network into smaller, distinct segments, each with exclusive security controls. This approach to cloud security curtails lateral movement, containing breaches within specific segments and enabling more customized security strategies to lower overall risk.
Continuous Monitoring: Zero Trust involves real-time monitoring of network activities to quickly detect and respond to threats. While it helps adapt to new threats, managing data volume and ensuring monitoring effectiveness can be challenging.
The Value of Adopting a Zero Trust Approach
Bolster Security: Implementing a Zero Trust architecture greatly improves an organization’s defense against numerous threats. Strict verification processes and adhering to the principle of least privilege significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Overcoming Advanced Threats: This robust cloud security model is highly effective against advanced persistent threats and insider attacks, areas where traditional perimeter defenses often fall short. Nonetheless, it’s essential to understand that zero trust’s effectiveness depends on accurate implementation and constant oversight.
Adapting Zero Trust to Any IT Environment: Zero Trust scales well across various IT environments, from small businesses to large enterprises with complex infrastructures. Its adaptability is key in today’s evolving digital landscape, though maintaining consistent security policies across diverse systems can be challenging.
Ensuring Trust and Compliance: Zero Trust helps meet data protection regulations by integrating with advanced cloud security platforms, enforcing strict access controls, and enhancing data monitoring. It supports compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA, boosting trust with customers and stakeholders.
Why Korcomptenz?
Korcomptenz delivers Zero Trust cloud security solutions designed for enterprises navigating multi-cloud environments. It handles secret management across diverse clouds as well as private data centers, enforcing security through identity controls, cloud security best practices, and upholding governance with comprehensive policies. Centralized access, storage, and distribution of dynamic secrets like passwords, tokens, certificates, and encoding keys are streamlined across any public or private cloud setting.
Embracing Managed Cloud Security Services
The emergence of Zero Trust architecture represents a crucial evolution in cybersecurity, addressing the need to secure increasingly distributed and dynamic ecosystems. By prioritizing the verification of every access request and the protection of singular resources, Zero Trust and advanced cloud security services provide a strong defense against contemporary cyber threats. As your business advances in the digital transformation journey, adopting Zero Trust cloud security solutions will be vital for protecting your critical assets and maintaining long-term resistance. Contact us for a free consultation.





